Occupational Therapy

Occupational Therapy or Ergotherapy (from Greek Ergon = work, therapeia = treatment) is a therapy based on engagement in purposeful everyday activities in order to restore, maintain or compensate for impairments or limitations of the patient’s health. Occupational therapy is designed to improve fine and general motor skills, pain control, and the development of cognitive functions. The therapy focuses on how the patients can be encouraged to return to normal daily activities, help them rehabilitate, or adapt to changes caused by illness or trauma. Patients are encouraged to achieve maximum functional independence in all areas of life, to facilitate the restoration of patients’ physical, mental, social, and professional abilities.
Ergotherapy is applied to patients of different ages for:
- musculoskeletal injuries (bone fractures) and diseases (osteoporosis, arthritis, osteoarthritis, etc.), accompanied by joint stiffness and contractures;
- nervous system disorders (head and spine injuries) and diseases (carpal tunnel syndrome, discogenic hernia, stroke, neuropathy, etc.) with sluggish paralysis;
- soft tissue injuries (scars that restrict hand movements; ligament, muscle, and tendon damage) and diseases (epicondylitis, tendovaginitis, etc.), muscle hypotrophy or atrophy, loss of strength.
Ergotherapy procedure can be:
- active;
- semi-active;
- passive.
The procedure helps:
- to increase the amplitude of movements
- to develop fine motor skills
- to strengthen weak muscles
- to improve blood supply to tissues
- to improve coordination and concentration
- the patient to become more independent
During the ergotherapy procedure, the patients are also taught how to ease their life and work activities when their physical abilities change; what exercises can be done at home and what tools found at home can be used to perform them. Patients are introduced to the principles of joint protection; how to avoid further negative impact on damaged structures (selection of splints, principles of work ergonomics, etc.); injury prevention and educating relatives. Knowledge gained by the patients helps them to help themselves independently in the present and in the future and improve their well-being. The exercises learned during the procedure help to continuously improve their physical condition after rehabilitation.
Depending on the functional and mental condition of the patient, the ergotherapy procedure can be performed with or without tools and with the help of electrostimulation devices. Various activities can be used to restore the impaired function, starting with children’s games (puzzles, blocks, silicone balls of different sizes and hardness, therapeutic masses, different resistance clips, resistance rubbers, etc.), basic household routines (button fastening, counting cents) to various devices and exercise equipment. The abundance of tools, devices, and modern equipment in the ergotherapy room ensures the variety of the procedure.
 E-LINK is an upper limb exerciser designed for people who need more effective restoration of upper limb function. During the procedure, the exercises are performed with a special device through games on a computer screen. The movements are evaluated and presented in statistical charts. The exerciser is suitable for patients of all ages, especially with the pathology of the wrist joint. The E-LINK exerciser is functional, the patient must use different types of gripping activities, use wrist movements in all possible amplitudes including the smallest joints. The exerciser has eleven different tool handles for performing movements that can be changed easily and quickly.
E-LINK is an upper limb exerciser designed for people who need more effective restoration of upper limb function. During the procedure, the exercises are performed with a special device through games on a computer screen. The movements are evaluated and presented in statistical charts. The exerciser is suitable for patients of all ages, especially with the pathology of the wrist joint. The E-LINK exerciser is functional, the patient must use different types of gripping activities, use wrist movements in all possible amplitudes including the smallest joints. The exerciser has eleven different tool handles for performing movements that can be changed easily and quickly.
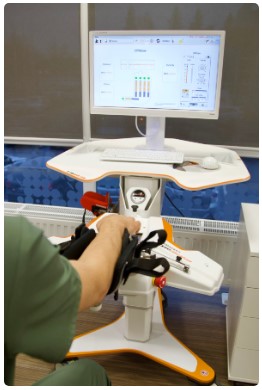
Tyromotion AMADEO® is a modern robotic finger-hand therapy system. This system is intended for the rehabilitation of patients with neurological disorders of the central nervous system (stroke or brain trauma), upper limb motor dysfunction or after injuries to the hands and fingers, and rheumatic diseases. AMADEO® performs assessment and treatment of spasticity, assessment and improvement of finger strength and mobility. It also has a mode for improving sensory sensation in the hand and fingers, improving and relaxing blood circulation, and with spasticity. The electronic movement mechanism of the AMADEO® system moves the fingers attached to special sliders which in turn move the thumbs and fingers of the right or left hand. Finger sliders can perform bending and stretching movements, individually or in sequences, with one finger or all together. The patient may be completely passive or be actively involved in therapy, depending on requirements or ability. Depending on the desired goal, various therapy modules (passive / semi-active improvement of finger mobility and strength with special programs or active mobility and strength training games) and movement parameters are individually selected. Exercise or interactive game therapy provides training and activation of finger strength, endurance, and movement. It also improves finger dexterity and reaction, grip, and release training, depending on finger strength or movement.

Tyromotion PABLO® is a modern therapy system for the rehabilitation of patients with motor and cognitive disorders. With the help of PABLO® system accessories and sensors, it is possible to measure the amplitudes of the shoulder and wrist joint, assess the grip of the hand and each finger, and monitor the patient’s progress during the rehabilitation period. During the interactive sessions, by selecting the desired movement with possible amplitude, both the mobility of certain structures is developed, as well as strength and endurance are improved. Each sensor has its own function: to improve the accuracy and control of hand grip, coordination of movement as well as to help integrate daily work and movements to perform work that is repeated many times and can be performed at different levels of difficulty. Such connection with daily work maintains patient motivation and helps restore motor functions. However, this is not the only advantage of the system. During interactive sessions, the patient’s cognitive functions and reaction are also developed (through special games), brain activity is activated, attention is diverted from pain because the patient experiences many positive emotions.

Tyromotion TYMO® is a sensor-based device for balance analysis assessment designed to obtain a quantitative assessment of balance and posture adjustment while standing. TYMO® strength sensors detect weight transfer and determine the centre of strength and body oscillation, load balancing above the feet. Based on this data, indicators of balance, stability, and symmetry are provided. Measurement results can provide insights into diagnosis and therapy. By integrating this device into interactive activities, the patient’s balance, movement coordination and body control are improved.
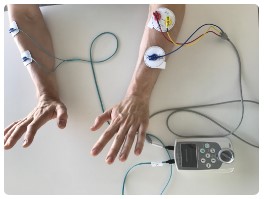
Occupational therapy with electrostimulation is a method that uses electrical impulses to produce muscle contraction or muscle relaxation. Stimulating the nerve-muscle connection promotes nerve healing, activates the processes in the muscles, improves metabolism, intensifies blood circulation, strengthens muscles. The procedures are performed using TENS NeuroTrac, REHAB NeuroTrac and IVES electrostimulation devices.

RehaDigit is a motor-operated therapy device for the treatment of hand and finger injuries or disability, and its alleviation. The device can be used in neurological patients, patients who have undergone hand surgery, injuries, etc. RehaDigit can effectively reduce muscle tone, restore lost sense of touch, and activate new movement possibilities. Using finger rollers, the patient’s fingers are bent and straightened. The vibration motor causes the hand to vibrate slightly, which helps to relax the finger muscles.
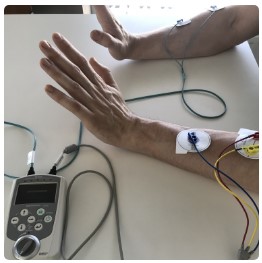
Electrical stimulator IVES GD-611 is a nerve and muscle stimulator that electrically stimulates these parts of the body through electrodes attached to certain parts of the body. The device has an EMG feedback detection function, so electrical stimulation can be proportional to the EMG feedback from the treated body parts. IVES GD-611 is designed to electrically stimulate the nerves and muscles of paralyzed patients with movement disorders or central nervous system problems, such as spinal cord injuries or after a stroke, using a surface electrode during rehabilitation.
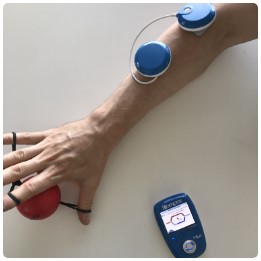
Compex Fit 5.0 is a wireless muscle stimulation device for the rehabilitation of patients with motor disorders. The target group consists of neurology, orthopaedic, and pediatric patients with movement and strength control, accuracy, coordination, bodily control, and balance disorders.
